Persuasive writing is a powerful tool in the world of communication, and mastering advanced clauses can elevate your persuasive skills to new heights. Whether you’re crafting a compelling argument, presenting a business proposal, or writing a thought-provoking essay, understanding how to effectively use advanced clauses can make your writing more impactful and convincing.
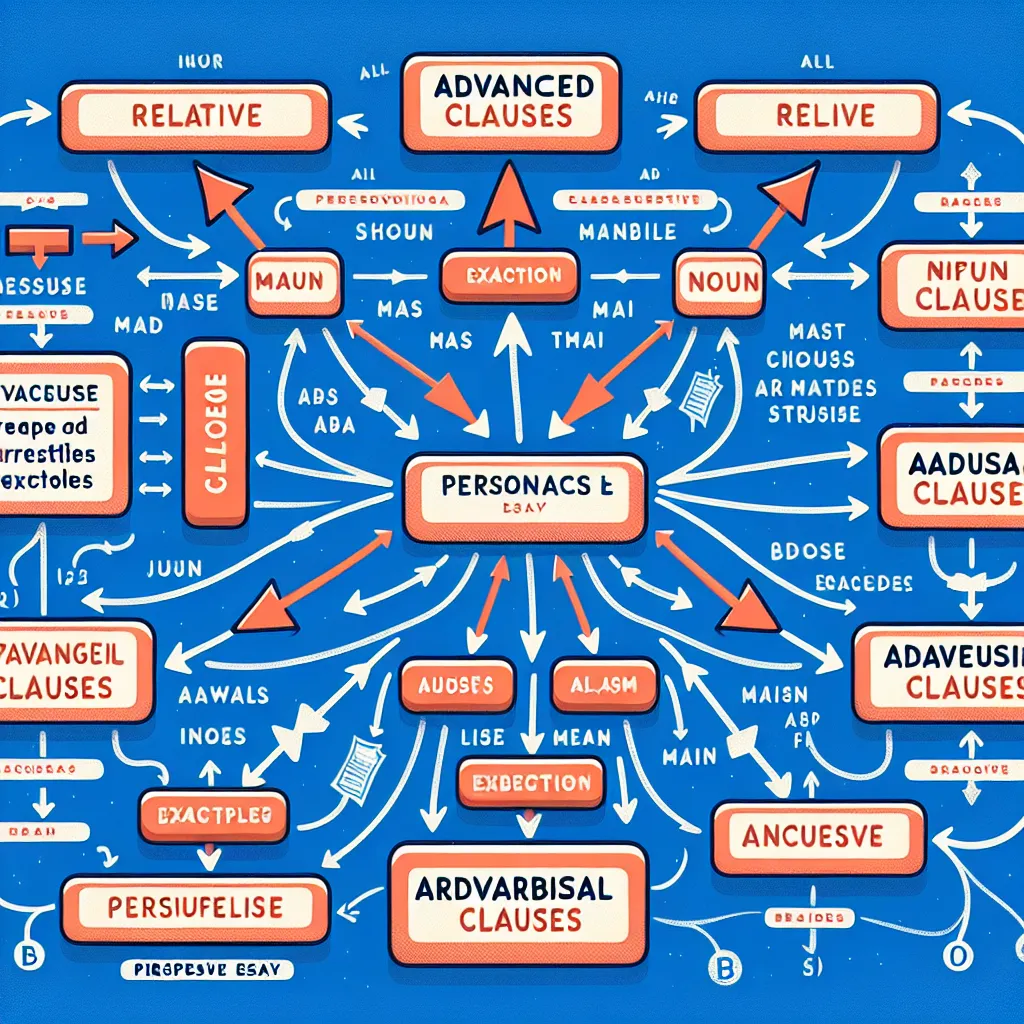 Advanced Clauses in Writing
Advanced Clauses in Writing
Understanding Advanced Clauses in Persuasive Writing
Advanced clauses are complex sentence structures that add depth, nuance, and sophistication to your writing. In persuasive writing, these clauses can help you present arguments more effectively, establish credibility, and create a more compelling narrative. Let’s explore how you can harness the power of advanced clauses to enhance your persuasive writing.
Types of Advanced Clauses for Persuasive Writing
-
Relative Clauses
- Definition: Clauses that provide additional information about a noun
- Example: “The proposal, which has been thoroughly researched, offers innovative solutions.”
- Effect: Adds credibility and specificity to your arguments
-
Noun Clauses
- Definition: Clauses that function as nouns in a sentence
- Example: “What we propose is a revolutionary approach to problem-solving.”
- Effect: Emphasizes key points and creates a strong focus
-
Adverbial Clauses
- Definition: Clauses that modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs
- Example: “While some may argue against this approach, the benefits far outweigh the risks.”
- Effect: Provides context and addresses potential counterarguments
Implementing Advanced Clauses in Your Persuasive Writing
To effectively use advanced clauses in your persuasive writing, consider the following strategies:
-
Vary Clause Types
Mix different types of clauses to create a dynamic and engaging writing style. For example:
“The solution we propose (noun clause), which has been tested extensively (relative clause), will significantly improve efficiency while reducing costs (adverbial clause).” -
Use Clauses to Build Logical Connections
Employ advanced clauses to establish clear relationships between ideas:
“Although initial implementation may be challenging (adverbial clause), the long-term benefits make it a worthwhile investment.” -
Emphasize Key Points with Cleft Sentences
Utilize cleft sentences to highlight important information:
“It is the innovative approach (noun clause) that sets our proposal apart from the competition.” -
Address Counterarguments
Use advanced clauses to acknowledge and refute opposing viewpoints:
“While some may argue that the cost is prohibitive (adverbial clause), the return on investment, which we’ve calculated meticulously (relative clause), justifies the initial expense.” -
Create Emotional Appeal
Incorporate advanced clauses to evoke emotions and connect with your audience:
“The children who will benefit from this program (relative clause) deserve every opportunity to succeed in life.”
 Persuasive Writing Example
Persuasive Writing Example
Practical Examples of Advanced Clauses in Persuasive Writing
Let’s examine a paragraph from a persuasive essay to see how advanced clauses can be effectively used:
“The proposal that we are presenting today (noun clause) offers a comprehensive solution to the challenges our city faces. While some may argue that the cost is too high (adverbial clause), we believe that the long-term benefits, which include reduced traffic congestion and improved air quality (relative clause), far outweigh the initial investment. It is through bold initiatives like this (cleft sentence with noun clause) that we can create a sustainable future for our community.”
In this example, we can see how different types of advanced clauses work together to create a compelling argument. The noun clause introduces the main topic, the adverbial clause addresses a potential counterargument, and the relative clause provides specific benefits. The cleft sentence emphasizes the importance of taking action.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
While advanced clauses can greatly enhance your persuasive writing, be cautious of these common mistakes:
- Overuse: Too many complex sentences can make your writing difficult to follow.
- Lack of variety: Using the same type of clause repeatedly can make your writing monotonous.
- Misplaced modifiers: Ensure that your clauses clearly relate to the intended subject.
- Unnecessary complexity: Sometimes, a simple sentence is more effective than a complex one.
Practicing Advanced Clause Usage
To improve your skills in using advanced clauses for persuasive writing, try these exercises:
- Rewrite simple sentences using different types of advanced clauses.
- Analyze persuasive texts from reputable sources, identifying and categorizing the advanced clauses used.
- Practice writing short persuasive paragraphs focusing on incorporating specific types of advanced clauses.
- Get feedback from peers or writing groups on your use of advanced clauses in persuasive pieces.
For more in-depth guidance on improving your grammar through writing, check out our article on how to improve grammar through writing.
Conclusion
Mastering the use of advanced clauses in persuasive writing is a powerful skill that can significantly enhance your ability to influence and convince. By understanding the different types of clauses and how to implement them effectively, you can create more sophisticated, nuanced, and compelling arguments. Remember to practice regularly and always consider your audience when crafting your persuasive pieces. With time and effort, you’ll find that advanced clauses become a natural and indispensable part of your persuasive writing toolkit.
To further enhance your writing skills, explore our article on advanced sentence structure tips, which complements the techniques discussed here.